Getting started
Look at our introductory articles about OpenHub framework on Java Code Geeks.
- Introducing OpenHub framework
- Asynchronous communication made by OpenHub framework
- Next Interesting Features - throttling, alerts, scheduled jobs, request/response tracking, error handling ...
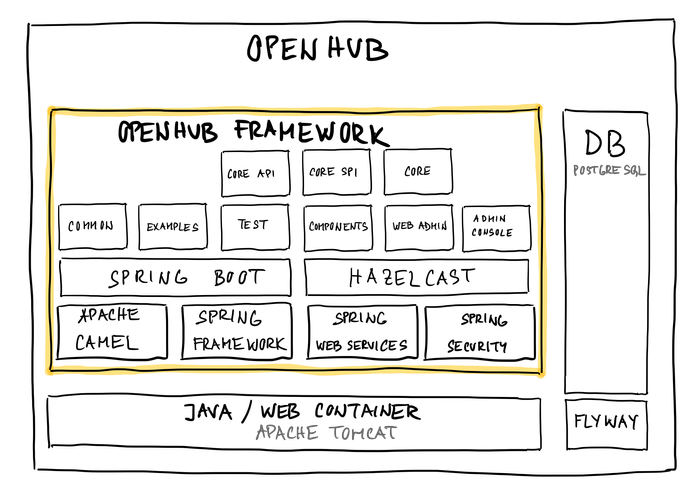
What is part of OpenHub framework?
Following diagram describes main technologies you came across when you start to develop with OpenHub framework. See Architecture section for more information.
What a developer needs to know?
Before you start playing with OpenHub framework look at libraries and tools which are part of our application stack:
- Java JDK
- Apache Maven (http://maven.apache.org)
- Apache Camel (http://camel.apache.org)
- JUnit (http://junit.org)
- Spring Boot (https://projects.spring.io/spring-boot/)
- Spring Framework (http://projects.spring.io/spring-framework)
- Spring Security (http://projects.spring.io/spring-security)
- security (authentication and autorization)
- Spring Web services (http://projects.spring.io/spring-ws)
- web services implementation
- web services implementation
- JAXB (https://jaxb.java.net/guide/ )
- XML marshalling/unmarshalling using by web services implementation
- Hibernate (http://hibernate.org) for persistence implementation
- Flyway (https://flywaydb.org) for schema/data migration
- Hazelcast (https://hazelcast.com) for caching
What a developer needs to install?
These are necessary:
- Java JDK 8, 9, 10, 11
- Apache Maven 3
- JAVA IDE
- Eclipse IDE for Java EE Developers (https://www.eclipse.org/downloads)
- Spring Tool Suite (http://spring.io/tools/sts)
- IntelliJ IDEA (http://www.jetbrains.com/idea/download/)
- Eclipse IDE for Java EE Developers (https://www.eclipse.org/downloads)
- all other needed libraries are fetched by Maven
These are optional:
- Apache Tomcat 8.0 and higher (http://tomcat.apache.org/) or JBOSS 7.1.0 EAP and higher
- PostgreSQL (http://www.postgresql.org/) – H2 DB is used by default, for JUnit tests run; for other types of deployment (standalone, Tomcat or others), PostgreSQL db datasource is used
- SoapUI (http://www.soapui.org/) for integration testing
IDE settings
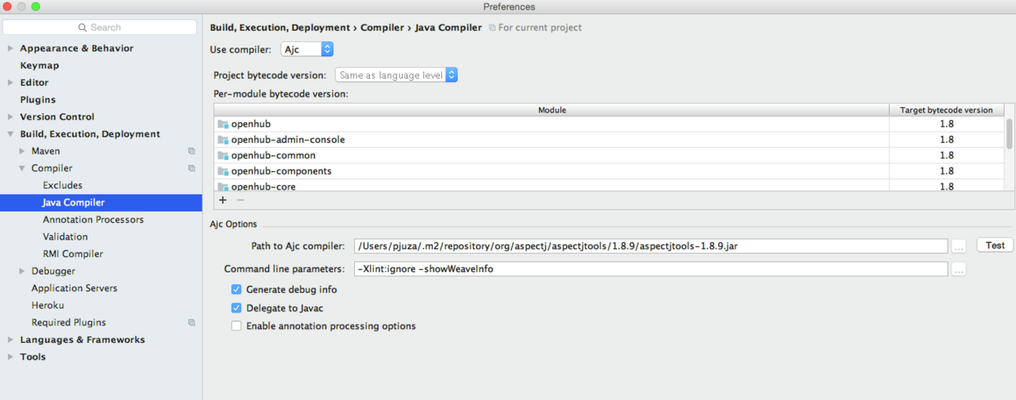
OpenHub framework is prepared to use AOP functionality. It's necessary to explicitly set up compilation by AspectJ in IDE.
Intellij IDEA
AspectJ compilation
We use compile-time weaving therefore it's necessary to set compilation by ajc.
Compile-time weaving is the simplest approach. When you have the source code for an application, ajc will compile from source and produce woven class files as output. The invocation of the weaver is integral to the ajc compilation process. The aspects themselves may be in source or binary form. If the aspects are required for the affected classes to compile, then you must weave at compile-time. Aspects are required, e.g., when they add members to a class and other classes being compiled reference the added members.
See IntelliJ IDEA help for more information.
Use same version of ajc in IDE and Maven.
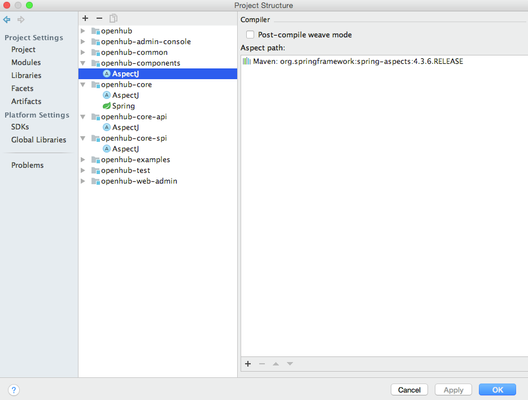
Aspect settings for AspectJ
Each module has dependency on Spring aspects which should be used during compilation (=compile-time weaving). Settings correspond to Maven configuration.
Debugging a code completion
Add the following plugins for full AOP support in IDE:
- AspectJ Support
- Spring AOP/@AspectJ
What next? Look at Reference implementation project or try building the OpenHub framework.